This diagram shows photoshop interface . It might help me for explaining my tips and designs ,and help you understanding what I mean. I tried my best to make it easy and understandably ..
I hope it will be helpful and useful for all of you.
Photo-shop interface [workspace] .Known as outside of the box.
- Menu bar:found on the top of the window. It contains the file,edit ,image and layer and other menus .
- Beside the Menu Bar there is the Application Bar showing the Hand Tool, Zoom Tool and Rotate View tool and Arrange Document and Screen Mode
- Tool Option bar :found under the menu bar.It shows the options of the selected tool .
- Tool box:by default it is found on the left side of the window.It shows the different photoshop tools
- Pallets:or pans it is found on the left side of the window.Like the layer pallet and color and others.
Select the Menu Bar >File>New or use shortcut Ctrl -N.A new dialog box will appear to choose width ,hight ,and also you will choose pixel ,cm or points .
Saving A File?
- Choose file save .From the format choose photoshop to keep all your layers.
- Save as to choose other format like JPEG or PNG or GIF or choose another place for the file .
- You can also save for web. to use on web pages ,it should be small in size and light for uploading.
WORKING WITH LAYERS.
- The best part about layers is that you can work with each layer separately without disturbing your art work.
- You can work with each layer separately or as a group [Layer >New >Group].
- Duplicating the layer[Ctrl-j] .
- To link layers together pressing on the layers you want to link together while holding the shift key to select the layers and click the link layers button at the bottom left of the layer palette .
- To unlink go to Layer > unlink layers.
- Rearrange the layers by drag and drop .
- To merge the layers Layer > merge(after selecting them) .Or by Ctrl-E.
Photoshop Tool [Panel ]Box.
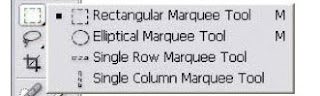
Selection Tools
- Rectangular Marquee Tool.To create rectangular or square shapes.
- Elliptical Marquee Tool .To create elliptical or circular shapes.
- Lasso Tool. To select the area around the shape you like.
- Polygonal Lasso Tool.
- Magnetic Lasso Tool.
- Quick Selection Tool.
- Magic Wand Tool .
- The Move Tool. To move the selected area
- The Crop Tool
- The Crop tool trims images.
- The Slice tool creates slices.
- The Slice Select tool selects slices.
Retouching tools .
- The Spot Healing Brush tool removes blemishes and objects .
- The Healing Brush tool paints with a sample or pattern to repair an image .
- The Patch tool repairs a selected area of an image using a sample or pattern.
- The Red Eye tool removes the red reflection caused by a flash .
- The Clone Stamp tool paints with a sample of an image .
- The Pattern Stamp tool paints with part of an image as a pattern.
- The Eraser tool erases pixels and restores parts of an image to a previously saved state.
- The Background Eraser tool erases areas to transparency by dragging.
- The Magic Eraser tool erases solid-colored areas to transparency with a single click.
- The Blur tool blurs hard edges in an image.
- The Sharpen tool sharpens soft edges in an image.
- The Smudge tool smudges data in an image.
- The Dodge tool lightens areas in an image.
- The Burn tool darkens areas in an image.
- The Sponge tool changes the color saturation of an area.
Painting tools.
- Brush Tool , paints brush strokes.
- Pencil Tool ,paints hard-edged strokes .
- The Color Replacement tool replaces a selected color with a new color.
- The History Brush tool paints a copy of the selected state or snapshot into the current image window.
- The Art History brush tool paints with stylized strokes that simulate the look of different paint styles, using a selected state or snapshot.
- The gradient tools create straight-line, radial, angle, reflected, and diamond blends between colors.
- The Paint Bucket tool fills similarly colored areas with the foreground color. under it there is Gradient Tool to allow the user to use the gradient colors
Drawing and type tools .
- The path selection tools make shape or segment selections showing anchor points, direction lines, and direction points.
- The type tools create type on an image.
- The type mask tools create a selection in the shape of type.
- The pen tools let you draw smooth-edged paths.
- The shape tools and Line tool draw shapes with colors , and lines in a normal layer or a shape layer.
- Rectangle Tool.
- Rounded Rectangle Tool .
- Ellipse Tool.
- Polygon Tool.
- Line shape Tool .
-Custom Shape Tool. - The Custom Shape tool makes customized shapes selected from a custom shape list.Thhat is my favorite tool .
Notes, measuring and navigation tools .
- The Eyedropper tool samples colors in an image.
- The Ruler tool is a measuring tool for distances, locations, and angles.
- The Note tool makes notes that can be attached to an image.
- The Counting tool counts objects in an image.
- The Hand tool moves an image within its window.
- The Zoom tool magnifies and reduces the view of an image.
- The Rotate View tool non-destructively rotates the canvas.
- The 3D Rotate tool ,rotates the model around its x-axis .
- The 3D Roll tool , rotates the model around its z-axis .
- The 3D Pan tool pans the camera in the x or y direction .
- The 3D Slide tool drags side to side to move the model horizontally, or up and down to move the model closer or farther away.
- The 3D Scale tool scales the model larger or smaller.
- The 3D Orbit tool orbits the camera in the x or y direction .
- The 3D Roll View tool rotates the camera around the z-axis .
- The 3D Pan View tool pans the camera in the x or y direction .
- The 3D Walk View tool walks the camera.
- The 3D Zoom tool changes the field of view closer or farther away.
How to use a tool ?
Do one of the following:
- Click a tool in the Tools panel.
- Press the tool’s keyboard shortcut.
COLOR SELECTION TOOLS .
- Color selection for background and foreground is very easy just click the tiles on the tool box to open the dialog box to choose the color you like .
- Eyedropper Tool . It is a very useful tool by which you can get a sample color from your photo. To use it click the eyedropper and click inside the document window . click with your cursor on the color you want to select .
Duplicate an image
duplicate an entire image including all layers, layer masks, and channels :
- Open the image
- Choose Image > Duplicate.
- Enter a name for the duplicated image.
Select Duplicate Merged Layers Only,
Click OK.
Transforming
- Retouching is helpful in many things to improve your picture or add or remove items and more other things .
- Transforming is using for scaling the size rotation and some other functions I will explain .
Adjusting crop, rotation, and canvas
Cropping an images:
It is the removing of a part of an image to create focus or strengthen it .It is done with the Crop Tool.
Crop an image using the Crop tool
- Select the Crop tool .
- With the mouth drag over the part of the image you want to keep to create a marquee.You can adjust ,move or scale and rotate it to the area you like to keep .
- press enter or check the right tick up.
Cropping options:
- Specify whether you want to use a cropping shield to shade the area of the image that will be deleted or hidden. When Shield is selected, you can specify a color and opacity for the cropping shield. When Shield is deselected, the area outside the cropping marquee is revealed.
- Specify whether you want to hide or delete the cropped area. Select Hide to preserve the cropped area in the image file it is better than deleting it so you can get it back if you like.The Hide option is not available for images that contain only a background layer so you can make layer from back ground by Rt click the background layer in the layer panel and choose layer from back ground.
I used that picture from the Egyptian desert .I think its nice.
Rotate or flip an entire image
The Image Rotation commands let you rotate or flip a hole image .It do not work on individual layers or part of a layers .For that purpose you can use the Transform or Free Transform Tools and commands .
Choose Image > Image Rotation, and choose one of the following from the submenu:
* 180° Rotates the image by a half-turn.
* 90° CW Rotates the image clockwise by a quarter-turn.
* 90° CCW Rotates the image counterclockwise by a quarter-turn.
* Arbitrary Rotates the image by the angle you specify .
Canvas Size.
It is the full editable area around the image.You can make a photo frame by increasing the canvas size and filling it with a color.
- Choose Image > Canvas Size.
- Enter the dimensions for the canvas in the Width and Height boxes,and choose the units of measurement .
- For Anchor, click a square to indicate where to position the existing image on the new canvas .
- Choose an option from the Canvas Color menu .
Make a frame for your image.
- You can make a photo frame by increasing the canvas size and filling it with a color.
- You can also make a styled photo frame ,It’s best to do this on a copy of your photo.
Retouching and repairing images
Retouch with the Clone Stamp tool
The Clone Stamp tool paints one part of an image over another part of the same image or over another part of any open document that has the same color mode. You can also paint part of one layer over another layer. The Clone Stamp tool is useful for duplicating objects or removing a defect in an image.You can also use the Clone Stamp tool to paint content on video or animation frames.
To use the Clone Stamp tool, you set a sampling point on the area you want to copy (clone) the pixels from and paint over another area.
You can use any brush tip with the Clone Stamp tool, which gives you good control over the size of the clone area.
How to use the tool.
- Select the Clone Stamp tool .
- Choose a brush tip and set brush options for the blending mode, opacity, and flow in the options bar.
- Samples data from the layers you specify. To sample from the active layer and visible layers below it, choose Current And Below. To sample only from the active layer, choose Current Layer. To sample from all visible layers, choose All Layers. To sample from all visible layers except adjustment layers, choose All Layers and click the Ignore Adjustment Layers icon to the right of the Sample pop-up menu.
- Alt-clicking the area you want to sample it .
- Drag over the area of the image you want to correct.
Retouch with the Healing Brush tool
The Healing Brush tool lets you correct imperfections, causing them to disappear from the image. You use the Healing Brush tool to paint with sampled pixels from an image or pattern.
How to use the tool.
Almost the same like the Clone Stamp tool .here you Drag in the image.
Notice: If there is a strong contrast at the edges of the area you want to heal, make a selection before you use the Healing Brush tool. The selection should be bigger than the area you want to heal but should precisely follow the boundary of contrasting pixels. When you paint with the Healing Brush tool, the selection prevents colors from bleeding in from the outside
Retouch with the Spot Healing Brush tool
It quickly removes blemishes and other imperfections in your photos.
The Spot Healing Brush works similarly to the Healing Brush: it paints with sampled pixels from an image or pattern and matches the texture, lighting, transparency, and shading of the sampled pixels to the pixels being healed. Unlike the Healing Brush, the Spot Healing Brush doesn’t require you to specify a sample spot. The Spot Healing Brush automatically samples from around the retouched area.If you need to retouch a large area or need more control over the source sampling, you can use the Healing Brush instead of the Spot Healing Brush.
How to use the tool.
- Select the Tool .
- Choose a brush size in the options bar. A brush that is slightly larger than the area you want to fix works better .
- Choose a Type option in the options bar:
Proximity Match
Uses the pixels around the edge of the selection to find an image area to use as a patch for the selected area. If this option doesn’t provide a satisfactory fix, undo the fix and try the Create Texture option.
Create Texture
Uses all the pixels in the selection to create a texture with which to fix the area. If the texture doesn't work, try dragging through the area a second time. - Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to sample data from all visible layers. Deselect Sample All Layers to sample only from the active layer.
- Click the area you want to fix, or click and drag to smooth over imperfections in a larger area
Patch an area
The Patch tool lets you repair a selected area with pixels from another area or a pattern.You can also use the Patch tool to clone isolated areas of an image.
Notice: When repairing with pixels from the image, select a small area to produce the best result.
- Repair an area using sampled pixels
- Select the Patch tool .
- Do one of the following:
•Drag in the image to select the area you want to repair, and select Source in the options bar.
•Drag in the image to select the area from which you want to sample, and select Destination in the options bar.
Notice : You can also make a selection prior to selecting the Patch tool.
- To adjust the selection, do one of the following:
•Shift-drag in the image to add to the existing selection.
•Alt-drag) in the image to subtract from the existing selection.
•Alt+Shift-drag in the image to select an area intersected by the existing selection.
- To extract texture with a transparent background from the sampled area, select Transparent.
- Deselect this option if you want to fully replace the target area with the sampled area.
Notice that the Transparent option works best for solid or gradient backgrounds with clearly distinct textures (such as a bird in a blue sky).
- Position the pointer inside the selection, and do one of the following:
- If Source is selected in the options bar, drag the selection border to the area from which you want to sample. When you release the mouse button, the originally selected area is patched with the sampled pixels.
- If Destination is selected in the options bar, drag the selection border to the area you want to patch. When you release the mouse button, the newly selected area is patched with the sampled pixels.
- Deselect this option if you want to fully replace the target area with the sampled area.
2 - Repair an area using a pattern
- Select the Patch tool .
- Drag in the image to select the area you want to repair.
Note: You can also make a selection prior to selecting the Patch tool.
- If desired, complete steps 3-4 above to adjust the selection and apply pattern texture with a transparent background.
- Select a pattern from the Pattern panel in the options bar, and click Use Pattern.
Remove red eyeNote: You can also make a selection prior to selecting the Patch tool.
The Red Eye tool removes red eye in flash photos of people or animals.
1- In RGB Color mode, select the Red Eye tool . (The Red Eye tool is in the same group as the Spot Healing Brush tool . Hold down a tool to display additional tools in the group.)
2- Click in the red eye. If you are not satisfied with the result, undo the correction, set one or more of the following options in the options bar, and click the red eye again:
Pupil Size
Increases or decreases the area affected by the Red Eye tool.
2- Click in the red eye. If you are not satisfied with the result, undo the correction, set one or more of the following options in the options bar, and click the red eye again:
Pupil Size
Increases or decreases the area affected by the Red Eye tool.
Replace color in image areas
The Color Replacement tool simplifies replacing specific colors in an image. You can paint over a targeted color with a corrective color. The Color Replacement tool doesn’t work in images in Bitmap, Indexed, or Multichannel color modes.
How to use the tool
1- Select the Color Replacement tool [under the Brush Tool] .
2- Choose a brush tip size in the options bar ,keep the blending mode set to Color
3- For the Sampling option, choose one of the following
- Continuous ,Samples colors continuously as you drag.
- Once ,Replaces the targeted color only in areas containing the color that you first click.
- Background Swatch ,Replaces only areas containing the current background color.
4- For the Limits option, select one of the following:
- Discontiguous ,Replaces the sampled color wherever it occurs under the pointer.
- Contiguous , Replaces colors that are contiguous with the color immediately under the pointer.
- Find Edges , Replaces connected areas containing the sampled color while better preserving the sharpness of shape edges.
5- For tolerance, enter a percentage value or drag the slider. Choose a low percentage to replace colors very similar to the pixel you click, or raise the percentage to replace a broader range of colors.
6- To define a smooth edge in the corrected areas, select Anti-aliased.
7- Choose a foreground color to replace the unwanted color.
8- Click the color you want to replace in the image.
9- Drag in the image to replace the targeted color.
Blending modes
- Normal : the default mode.Edits or paints each pixel to make it the result color.
- Dissolve: the result color is a random replacement of the pixels with the base color or the blend color, depending on the opacity at any pixel location.
- Behind : Edits or paints only on the transparent part of a layer .
- Clear : Edits or paints each pixel and makes it transparent.
- Darken : make the color darker.
- Multiply: Multiplying any color with black produces black.
- Color Burn : increasing the contrast,with white no change .
- Linear Burn : decreasing the brightness. with white no change.
- Lighten : Pixels darker than the blend color are replaced, and pixels lighter than the blend color do not change .
- Screen : The result color is always a lighter color, with black leaves the color unchanged.
- Color Dodge : decreasing contrast , with black produces no change.
- Linear Dodge (Add) : increasing the brightness, with black produces no change.
- Overlay : Multiplies or screens the colors, depending on the base color.The base color is not replaced, but mixed with the blend color to reflect the lightness or darkness of the original color.
- Soft Light : Darkens or lightens the colors.
- Hard Light : The effect is similar to shining a strong spotlight on the image.This is useful for adding highlights to an image.
- Vivid Light: Burns or dodges the colors by increasing or decreasing the contrast.
- Linear Light : Burns or dodges the colors by decreasing or increasing the brightness.
- Pin Light : Replaces the colors. This is useful for adding special effects to an image.
- Hard Mix : Adds the red, green and blue channel values of the blend color to the RGB values of the base color.
- Difference : subtracts either the blend color from the base color or the base color from the blend color, depending on which has the greater brightness value.
- Exclusion : Creates an effect similar to but lower in contrast than the Difference mode. Blending with white inverts the base color values. Blending with black produces no change.
- Hue : Creates a result color with the luminance and saturation of the base color and the hue of the blend color.
- Saturation.
- Color.
- Luminosity : Creates a result color with the hue and saturation of the base color and the luminance of the blend color. This mode creates the inverse effect of Color mode.
- Lighter Color .
- Darker Color .
Smudge image areasSimulates the effect of dragging a finger through wet paint .The tool picks up color where the stroke begins and pushes it in the direction you drag.
How to use the tool 1 - Select the Smudge tool .
2 - Choose a brush tip and options for the blending mode in the options bar.
3 - Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to smudge using color data from all visible layers. If this is deselected, the Smudge tool uses colors from only the active layer.
4 - Select Finger Painting in the options bar to smudge using the foreground color at the beginning of each stroke. If this is deselected, the Smudge tool uses the color under the pointer at the beginning of each stroke.
5 - Drag in the image to smudge the pixels.
Blur image The Blur tool softens hard edges or reduces detail in an image. The more you paint over an area with the tool, the more blur it becomes .
How to use the tool 1 - Select the Blur tool .
2 - Do the following in the options bar:- Choose a brush tip and set options for the blending mode and strength in the options bar
- Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to blur using data from all visible layers. If this is deselected, the tool uses data from only the active layer.
3 - Drag over the part of the image you want to blur.[ you can also use the blur filter in the filter menu]
Sharpen image The Sharpen tool increases contrast along edges to increase apparent sharpness. The more you paint over an area with the tool, the sharpen effect increases.1-Select the Sharpen tool .
2-Do the following in the options bar:
•Choose a brush tip and set options for the blending mode and strength in the options bar.
•Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to sharpen using data from all visible layers. If this is deselected, the tool uses data from only the active layer.
3Drag over the part of the image you want to sharpen.
Dodge or burn areas Used to lighten or darken areas of the image[ lighten an area on the print (dodging) or increase the exposure to darken areas on a print (burning).]more you paint over an area with the Dodge or Burn tool, the lighter or darker it becomes.
1- Select the Dodge tool or the Burn tool. 2-Choose a brush tip and set brush options in the options bar. 3- In the options bar, select one of the following from the Range menu: - Midtones :Changes the middle range of grays.
- Shadows :Changes the dark areas.
- Highlights :Changes the light areas.
4-Specify the exposure for the Dodge tool or the Burn tool.5-Click the airbrush button to use the brush as an airbrush. Alternatively, select the Airbrush option in the Brushes panel.6-Select the Protect Tones option to minimize clipping in the shadows and highlights. This option also tries to keep colors from shifting hue.
7-Drag over the part of the image you want to lighten or darken.
Adjust color saturation in image areas The Sponge tool changes the color saturation of an area. When an image is in Grayscale mode, the tool increases or decreases contrast by moving gray levels away from or toward the middle gray. 1-Select the Sponge tool .
2-Choose a brush tip and set brush options in the options bar.
3-In the options bar, choose the way you want to change the color from the Mode menu:
Saturate :Intensifies the color’s saturation.
Desaturate :Dilutes the color’s saturation.
4-Specify the flow for the Sponge tool.
5-Select the Vibrance option to minimize clipping for fully saturated or desaturated colors.
6-Drag over the part of the image you want to modify.
NEXT TIP Adjusting image sharpness and blur
2- Choose a brush tip size in the options bar ,keep the blending mode set to Color
3- For the Sampling option, choose one of the following
- Continuous ,Samples colors continuously as you drag.
- Once ,Replaces the targeted color only in areas containing the color that you first click.
- Background Swatch ,Replaces only areas containing the current background color.
- Discontiguous ,Replaces the sampled color wherever it occurs under the pointer.
- Contiguous , Replaces colors that are contiguous with the color immediately under the pointer.
- Find Edges , Replaces connected areas containing the sampled color while better preserving the sharpness of shape edges.
6- To define a smooth edge in the corrected areas, select Anti-aliased.
7- Choose a foreground color to replace the unwanted color.
8- Click the color you want to replace in the image.
9- Drag in the image to replace the targeted color.
- Normal : the default mode.Edits or paints each pixel to make it the result color.
- Dissolve: the result color is a random replacement of the pixels with the base color or the blend color, depending on the opacity at any pixel location.
- Behind : Edits or paints only on the transparent part of a layer .
- Clear : Edits or paints each pixel and makes it transparent.
- Darken : make the color darker.
- Multiply: Multiplying any color with black produces black.
- Color Burn : increasing the contrast,with white no change .
- Linear Burn : decreasing the brightness. with white no change.
- Lighten : Pixels darker than the blend color are replaced, and pixels lighter than the blend color do not change .
- Screen : The result color is always a lighter color, with black leaves the color unchanged.
- Color Dodge : decreasing contrast , with black produces no change.
- Linear Dodge (Add) : increasing the brightness, with black produces no change.
- Overlay : Multiplies or screens the colors, depending on the base color.The base color is not replaced, but mixed with the blend color to reflect the lightness or darkness of the original color.
- Soft Light : Darkens or lightens the colors.
- Hard Light : The effect is similar to shining a strong spotlight on the image.This is useful for adding highlights to an image.
- Vivid Light: Burns or dodges the colors by increasing or decreasing the contrast.
- Linear Light : Burns or dodges the colors by decreasing or increasing the brightness.
- Pin Light : Replaces the colors. This is useful for adding special effects to an image.
- Hard Mix : Adds the red, green and blue channel values of the blend color to the RGB values of the base color.
- Difference : subtracts either the blend color from the base color or the base color from the blend color, depending on which has the greater brightness value.
- Exclusion : Creates an effect similar to but lower in contrast than the Difference mode. Blending with white inverts the base color values. Blending with black produces no change.
- Hue : Creates a result color with the luminance and saturation of the base color and the hue of the blend color.
- Saturation.
- Color.
- Luminosity : Creates a result color with the hue and saturation of the base color and the luminance of the blend color. This mode creates the inverse effect of Color mode.
- Lighter Color .
- Darker Color .
Smudge image areas
Simulates the effect of dragging a finger through wet paint .The tool picks up color where the stroke begins and pushes it in the direction you drag.
How to use the tool
How to use the tool
1 - Select the Smudge tool .
2 - Choose a brush tip and options for the blending mode in the options bar.
3 - Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to smudge using color data from all visible layers. If this is deselected, the Smudge tool uses colors from only the active layer.
4 - Select Finger Painting in the options bar to smudge using the foreground color at the beginning of each stroke. If this is deselected, the Smudge tool uses the color under the pointer at the beginning of each stroke.
5 - Drag in the image to smudge the pixels.
2 - Choose a brush tip and options for the blending mode in the options bar.
3 - Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to smudge using color data from all visible layers. If this is deselected, the Smudge tool uses colors from only the active layer.
4 - Select Finger Painting in the options bar to smudge using the foreground color at the beginning of each stroke. If this is deselected, the Smudge tool uses the color under the pointer at the beginning of each stroke.
5 - Drag in the image to smudge the pixels.
Blur image
The Blur tool softens hard edges or reduces detail in an image. The more you paint over an area with the tool, the more blur it becomes .
How to use the tool
1 - Select the Blur tool .
2 - Do the following in the options bar:
2 - Do the following in the options bar:
- Choose a brush tip and set options for the blending mode and strength in the options bar
- Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to blur using data from all visible layers. If this is deselected, the tool uses data from only the active layer.
3 - Drag over the part of the image you want to blur.
[ you can also use the blur filter in the filter menu]
Sharpen image
The Sharpen tool increases contrast along edges to increase apparent sharpness. The more you paint over an area with the tool, the sharpen effect increases.
1-Select the Sharpen tool .
2-Do the following in the options bar:
•Choose a brush tip and set options for the blending mode and strength in the options bar.
•Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to sharpen using data from all visible layers. If this is deselected, the tool uses data from only the active layer.
3Drag over the part of the image you want to sharpen.
2-Do the following in the options bar:
•Choose a brush tip and set options for the blending mode and strength in the options bar.
•Select Sample All Layers in the options bar to sharpen using data from all visible layers. If this is deselected, the tool uses data from only the active layer.
3Drag over the part of the image you want to sharpen.
Dodge or burn areas
Used to lighten or darken areas of the image[ lighten an area on the print (dodging) or increase the exposure to darken areas on a print (burning).]more you paint over an area with the Dodge or Burn tool, the lighter or darker it becomes.
1- Select the Dodge tool or the Burn tool.
2-Choose a brush tip and set brush options in the options bar.
3- In the options bar, select one of the following from the Range menu:
- Midtones :Changes the middle range of grays.
- Shadows :Changes the dark areas.
- Highlights :Changes the light areas.
4-Specify the exposure for the Dodge tool or the Burn tool.
5-Click the airbrush button to use the brush as an airbrush. Alternatively, select the Airbrush option in the Brushes panel.
6-Select the Protect Tones option to minimize clipping in the shadows and highlights. This option also tries to keep colors from shifting hue.
7-Drag over the part of the image you want to lighten or darken.
Saturate :Intensifies the color’s saturation.
Desaturate :Dilutes the color’s saturation.
4-Specify the flow for the Sponge tool.
5-Select the Vibrance option to minimize clipping for fully saturated or desaturated colors.
6-Drag over the part of the image you want to modify.
NEXT TIP Adjusting image sharpness and blur
7-Drag over the part of the image you want to lighten or darken.
Adjust color saturation in image areas
The Sponge tool changes the color saturation of an area. When an image is in Grayscale mode, the tool increases or decreases contrast by moving gray levels away from or toward the middle gray.
1-Select the Sponge tool .
2-Choose a brush tip and set brush options in the options bar.
3-In the options bar, choose the way you want to change the color from the Mode menu:
2-Choose a brush tip and set brush options in the options bar.
3-In the options bar, choose the way you want to change the color from the Mode menu:
Saturate :Intensifies the color’s saturation.
Desaturate :Dilutes the color’s saturation.
4-Specify the flow for the Sponge tool.
5-Select the Vibrance option to minimize clipping for fully saturated or desaturated colors.
6-Drag over the part of the image you want to modify.
NEXT TIP Adjusting image sharpness and blur







